About
URANIUM MARKET
The Rising Demand for Uranium in the Global Clean Energy Transition
The urgent need for a sustainable energy future, the global clean energy transition has intensified the search for alternative fuel sources. Nuclear power stands out as a crucial component in the fight against climate change with its exceptional ability to generate large amounts of energy with minimal carbon emissions. According to various studies, nuclear power not only has the lowest carbon footprint among all energy sources, but it also provides a reliable option for baseload electricity, which is essential for modern energy systems. As societies seek to phase out their dependence on fossil fuels, the demand for uranium—the key fuel for nuclear reactors—has surged.
Fig 1. Illustration of Uranium Energy Efficiency (Source: US Department of Energy)
A Complex Supply Landscape
The road to securing a sustainable uranium supply is fraught with challenges. The global uranium landscape has been significantly affected by a range of geopolitical events and economic factors that adversely impacted production levels. Over the past decade, a combination of fluctuating prices, mine closures, and operational disruptions has created a scenario of reduced supply.
One of the lingering impacts of these dynamics has been a notable underinvestment in uranium mining operations. The reduction in capital flow into new exploration and development projects has contributed to what many experts term a "structural deficit" in uranium supply. This deficit is characterized by a significant gap between the increasing global demand for uranium—driven by the burgeoning nuclear power sector—and the available production capacity.
Compounding these supply constraints is the strategy of various market actors, including uranium producers, developers, and physical holding companies, who have increasingly turned to purchasing physical uranium as an investment. This trend has only heightened the strain on an already stressed supply chain. The competition for available uranium has risen, thereby pushing prices up and signaling an urgent need for new production and investment strategies to meet future demands.
Global Commitment to Nuclear Energy
At the 2023 United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP 28), 22 countries acknowledged the essential role of nuclear energy in their energy security and affordability strategies, committing to an ambitious plan to triple nuclear capacity by 2050. This development demonstrates a collective understanding that nuclear power is indispensable in the transition to clean energy.
Currently, there are 440 operating reactors across 31 countries, plus an additional 60 Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) under construction in 18 countries. The World Nuclear Association’s Nuclear Fuel Report of 2023 anticipates that without new uranium entering the market, demand will outstrip supply within the next decade, primarily as a result of expanding nuclear power programs.
The Promising Role of Small Modular Reactors (SMRs)
Nuclear power has a crucial role to play on the path to net zero. Traditional nuclear plants, however, can be costly, resource-intensive, and take up to 12 years to come online. Small modular reactors (SMR) offer a possible solution. Small modular reactors (SMRs) are advanced nuclear reactors that have a power capacity of up to 300 MW(e) per unit, which is about one-third of the generating capacity of traditional nuclear power reactors.1
Figure 2. Small Module Reactor Illustration
Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) are positioned to play a pivotal role in meeting the future energy needs efficiently and cost-effectively. compelling advantages that SMRs offer include:
1. Lower Costs
- SMRs require less upfront capital due to their smaller size and modular design, which also allows them to compete with traditional reactors on a per-unit electricity cost basis. Economic efficiencies arise from factory fabrication and design simplifications.
2. Quicker Deployment
- While traditional nuclear plants can take up to 12 years to become operational due to their site-specific designs, SMRs can be produced largely in factories and deployed in as little as three years. This expeditious deployment is crucial for meeting the immediate electricity demands in a transitioning economy.
3. Siting Flexibility and Land Efficiency
- SMRs possess a greater siting flexibility due to their compact size and can generate a higher output of electrical energy per unit of land area compared to larger reactors. They can also be installed at decommissioned coal power plant sites, maximizing existing infrastructure.
4. Enhanced Safety
- The simpler designs of SMRs, along with passive cooling systems and lower operating pressures, provide an inherent safety advantage over traditional reactors. Additionally, they have extended refueling needs, which reduces transportation requirements and risk.
Government Policies Driving Change
Government policies are pivotal in reshaping nuclear markets. With a growing focus on energy independence and ethical supply chains as indicators of national security, several international measures have been enacted. The U.S. government, for instance, established the “Prohibiting Russian Uranium Imports Act” in May 2024, limiting imports from its largest foreign supplier. Similarly, the “ADVANCE Act” was implemented in July 2024 to fortify American energy security and promote nuclear power as a reliable clean energy source.
The geopolitical landscape also affects the uranium market. Notably, Niger, which accounted for about 5% of global uranium production, recently underwent political upheaval following a coup in 2023.2 With the new government demanding the expulsion of U.S. and French forces, the instability highlights the inherent risks associated with sourcing uranium from politically volatile regions, reinforcing the necessity for diversified and secure supply chains.
Geopolitical Events Affecting the Uranium Market
| DATE | EVENT 3 |
| December 4, 2020 | US Senate committee approves uranium reserve bill |
| December 16, 2022 | First contracts awarded for US strategic uranium reserve |
| March 6, 2023 | Nuclear power revival reaches Japan, home of the last meltdown |
| November 15, 2023 | Kazatomprom signs long-term uranium supply contract with China |
| December 10, 2023 | China uranium grab poses threat to western energy supply, warns Yellow Cake Plc. |
| December 27, 2023 | Japan lifts operational ban on world's biggest nuclear plant |
| January 9, 2024 | DOE announces next steps to build domestic uranium supply for advanced nuclear reactors as part of President Biden's Investing in America Agena. |
| April 30, 2024 | US Senate approves bill to ban Russian uranium imports |
| May 27, 2024 | Russia will build Central Asia's first nuclear power plant in an agreement with Uzbekistan |
| May 29, 2024 | Hungary's government signs deal with Belarus to help build nuclear reactor |
| August 23, 2024 | Kazatomprom, the world's largest uranium producer, announces that the production volume for its mining operations will be approximately 20% below levels stipulated in its agreements |
| September 20, 2024 | Constellation announces plan to restart Three Mile Island Nuclear Plant with Microsoft entering into 20-year power purchase agreement |
Uranium Drivers – Electricity
The uranium market is currently being driven, in part, by a macro demand for more electricity generation and a push to decarbonize electrical grids. According to the International Energy Agency (“IEA”), Canada’s electricity generation is over 80% renewable sources and nuclear, while China and Australia’s electricity generation is over 75% coal, oil and natural gas.
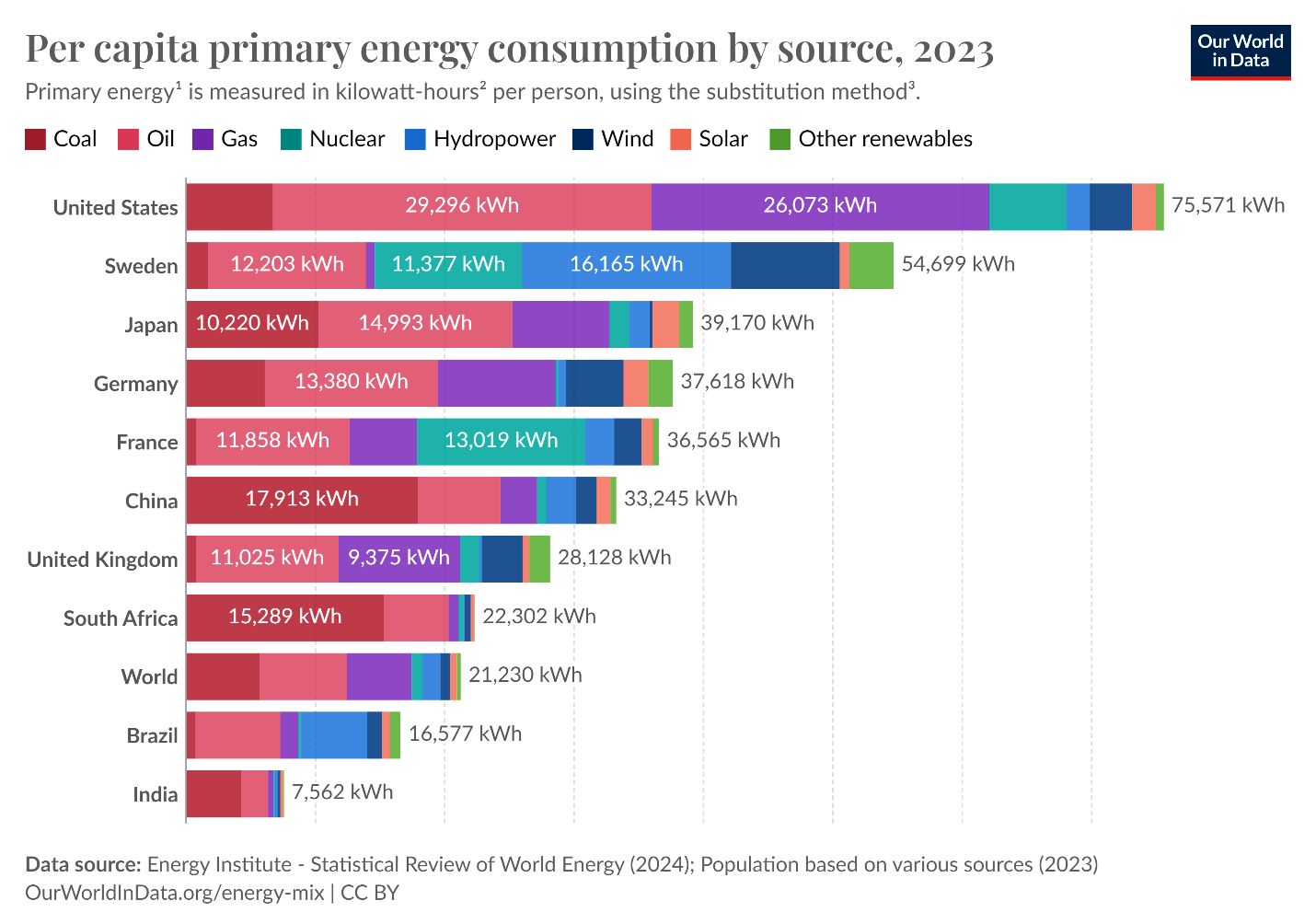
Figure 3. IEA’s Global Energy Consumption by Source, per Country
According to the IEA, global electricity demand is expected to rise at a rate of 3.4% annually over the next three years as countries try and meet their net zero emissions and decarbonization targets. The gains will be primarily driven by an improving economic outlook, contributing to faster electricity demand growth in advanced and emerging economies.
Electricity consumption from data centres, artificial intelligence (AI) and the cryptocurrency sector could double by 2026. Data centres are significant drivers of growth in electricity demand in many regions. After globally consuming an estimated 460 terawatt-hours (TWh) in 2022, data centres’ total electricity consumption could reach more than 1 000 TWh in 2026.
Uranium Pricing
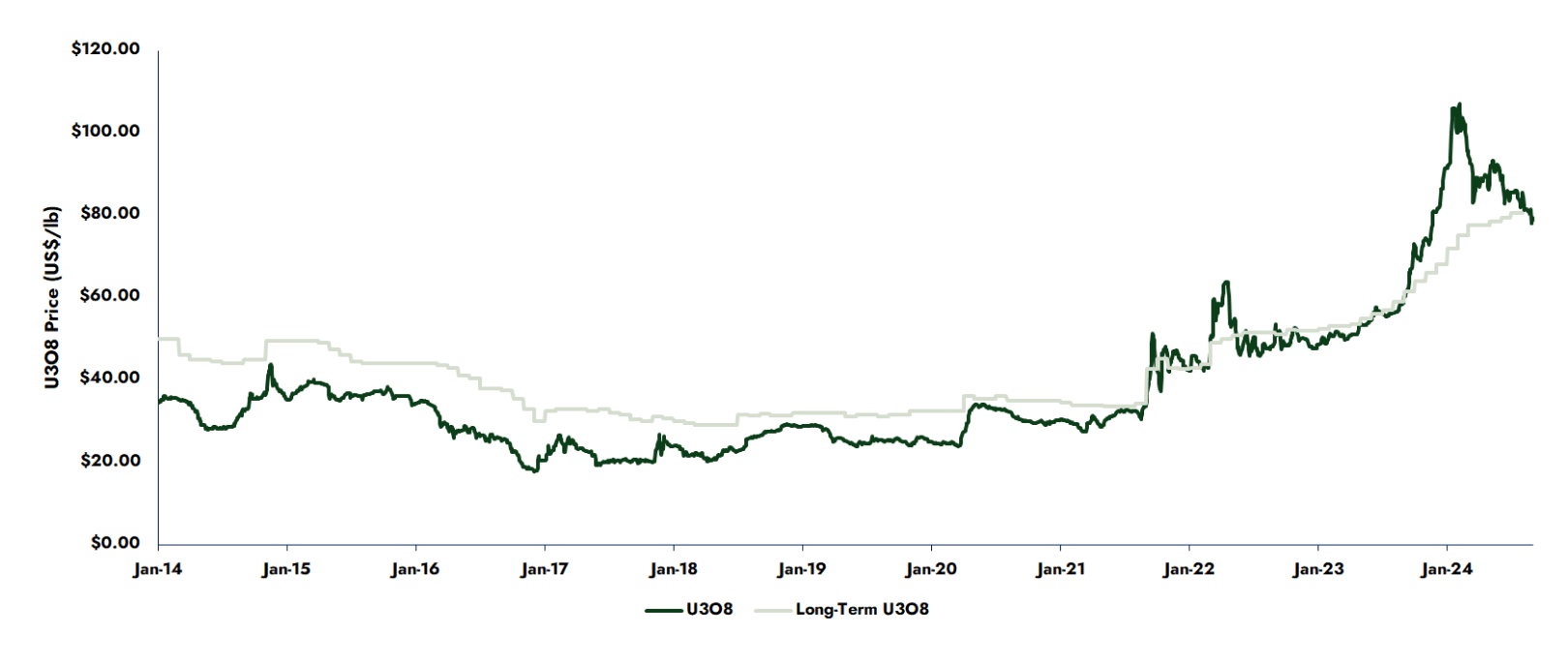
Over the past few years global uranium market fundamentals have improved as the market began a transition from being an inventory driven market to a production driven one. While the spot market bottomed out in November 2016 at approxamitely $17.75 per pound U3O8, it has since rebounded , reaching $107.00 per pound U3O8 on February 2, 2024.
Expected realized uranium price sensitivity under various spot price assumptions at June 30, 2024 are in the table below
| Spot Prices ($US/lb U3O8) |
$20 | $40 | $60 | $80 | $100 | $120 | $140 |
| 2024 | 49 | 52 | 55 | 57 | 58 | 59 | 59 |
| 2025 | 39 | 44 | 54 | 61 | 64 | 65 | 65 |
| 2026 | 42 | 44 | 56 | 67 | 69 | 70 | 72 |
| 2027 | 43 | 45 | 58 | 69 | 73 | 74 | 76 |
| 2028 | 46 | 49 | 58 | 70 | 75 | 77 | 78 |
Table 1. (Rounded to the nearest $1.00. Table information sourced from Cameco)
Government policies, supply/demand issues, and the global desire for electrification continue to influence and drive the global energy mix. A renewed focus on nuclear power to provide energy security has become widespread. It seems conclusive that the world will require increased uranium exploration and development in the years to come.
In Conclusion
As we stand at the intersection of environmental responsibility and energy demand, the significance of secure, reliable, and green energy sources has never been greater. Nuclear power—bolstered by advanced frameworks like Small Modular Reactors—will play an essential role in our transition to a clean energy future. However, responsibility must be taken to address the supply side of uranium production urgently. Ongoing uranium by companies such as Foremost Clean Energy is essential to guarantee that nuclear power can deliver on its potential within a sustainable global energy framework.
1. Visual Capitalist: The Four Benefits of Small Modular Reactors
2. https://payneinstitute.mines.edu/niger-uranium-and-the-coup-detat/
3. Source: FactSets Insights, May 2024